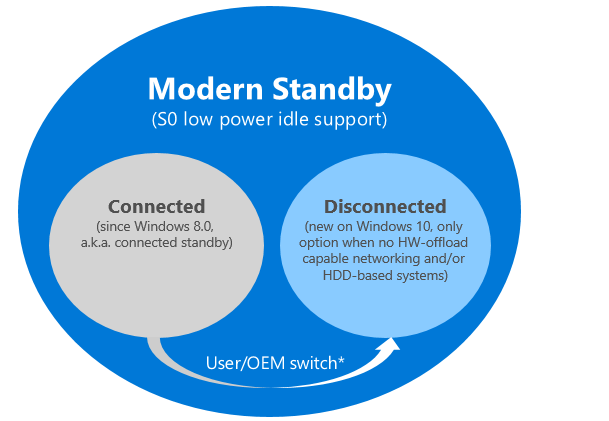
What is Modern Standby power mode
There are two primary goals that Modern Standby fulfills are: It includes pure rotational media and hybrid media (SSD + HDD or SSHD) and NIC without offload capability. This way, it allows more computers to make use of the Modern Standby mode. Modern Standby offers two modes— The former is the same as Connected Standby, but the later was introduced in Windows 10. It comes into action when there is no hardware offload capable networking or its an HDD based system. HDDs are still cheaper compared to SSDs. It is the primary reason why Microsoft has introduced the disconnected method. A business with HDD and backup plans in place will spend less money compared to buying SSDs.
Modern Standby & Hardware compatibility
In simple words, If an SSD or SSD+HDD and NIC are connected, which can offload, it uses Connected Standby mode. If it is a rotational media (Only HDD), then it will use the Disconnected mode. Both modes allow background activity for local triggers and devices, but in the case of Disconnected mode, the system will not receive any network events. While pure SSD with Offload Capable WLAN offers the best experience, a system with a Hybrid SSD + HDD combination with Offload Capable WLAN is the best tradeoff. It offers more storage but with no network events. The table above is from the Channel 9 Presentation on Modern Standby Overview
How does Modern Standby works
As soon as the system enters into Sleep Mode, the OS prepares both the software and the hardware for a low-power operation state. First comes the turn for software, and then the hardware, which also includes device drivers. To make sure that the least amount of power is consumed, the mode only allows the software to execute in short, controlled bursts. The OS and the SoC hardware will always listen to events such as incoming packets or input from the keyboard and will wake up the computer instantly. It can also wake up the entire system if a scheduled backup is triggered. During the Modern standby mode, Windows goes from idle mode to active mode to perform kernel maintenance tasks. It lasts for a few hundred milliseconds. However, networking devices switch between active and lower power states based on software activity. If there is an incoming email or Windows starts downloading an update, then the active period can be longer. When the computer receives an input like the press of the power button, it typically takes less than 500 milliseconds for the system to come online. It restores all applications and hardware status to active mode.
Find if your Windows PC supports Modern Standby
Open the Command Prompt with admin privileges. Type the following command and press Enter: You may also use powercfg /a instead. This command reports the sleep states available on the system and attempts to report reasons why sleep states are unavailable. On my computer, it shows S2 and S0 are not available. S0 (Zero) is the Modern Standby or the Connected Standby mode. While other modes, including S1, S3, Hibernate, Hybrid Sleep, and Fast Startup is available. While “S0” can mean connected standby mode as well, in the end, it will depend on the hardware of the computer. Match the hardware with the table, and you will know which modern Standby is supported. I hope the post was able to explain Modern Standby, and helped you to figure out if your Windows PC supports it. Next, we will see how to Enable Network Connections while in Modern Standby. Related reads: