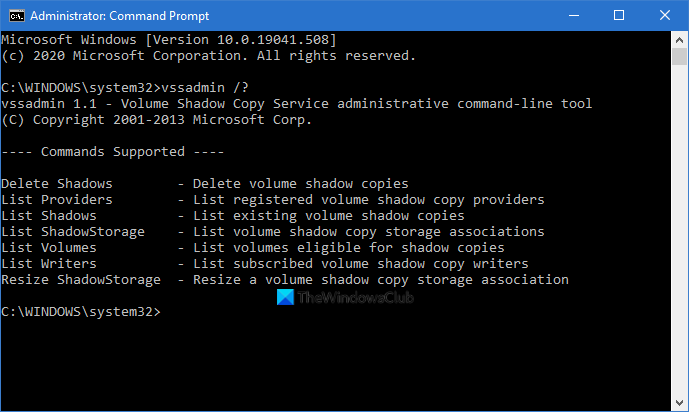
It has a library of associated commands for listing shadow copy writers and providers, creating and deleting VSS associations and copies, as well as resizing VSS associations. This post shows you how to effectively make use of these commands.
VSS components
Before delving into how to manage VSS using Vssadmin, we’ll first have a look at the various components of the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS). Thanks to the use of shadow copies or snapshots, these components let you perform crucial operations, such as backing up your server in a way that doesn’t affect logged-in users or running programs. Let’s explore the various VSS components and the tasks they perform on your server.
1] VSS requester
Examples of VSS requesters include the System Center Data Protection Manager and the Windows Server Backup program. The primary function of these components is to request for the VSS to take a shadow copy.
2] VSS writer
Windows Servers can have several VSS writers. These are components that the application software provides to ensure that the data is set for creating shadow copies. Some examples of VSS writers include the following:
WMI WriterRegistry WriterHyper-VExchange ServerPerformance Counter WriterNTDS WriterSystem WriterDHCP Jet WriterSQL ServerActive Directory System ServiceASR WriterWINS Jet WriterCertificate Authority Writer
… etcetera.
3] Storage volume
A storage volume is a crucial component of the VSS that holds the data that you are about to copy.
4] VSS provider
VSS providers are included in storage arrays provided by hardware vendors. They create and manage shadow copies. Some examples of VSS providers are the Microsoft Software Copy provider and the Microsoft File Share Shadow Copy provider.
5] Source volume
A source volume is where the system keeps the shadow copy storage files that the VSS provider uses. Now that you know the VSS components, let’s take a look at how they work. Here, I’ll give an overview of the Vssadmin commands and how you can use them to manage the VSS.
Using Vssadmin command-line to manage VSS
To manage VSS using the Vssadmin command-line tool, you first need to log in to the server as an administrator. When you’re in, launch Command Prompt with administrative privileges. Search for Command Prompt, right-click it, and choose Run as Administrator. When in the elevated Command Prompt, below are the commands for managing VSS. To run any, type it out and press ENTER. You use the above commands with syntax and switches. These specify system volumes on which to carry out the action. They also streamline the commands. Below are the various parameters for Vssadmin. You can read more about this at TechNet.